Data Source Tree
Contents Hide
The Data Source tree is a very essential element in BrightBuilder. All data sources in a project are made available in this tree. These data sources are used in expressions, as parameters in Methods, as condition operands in data validation rules, and as parameters for parameterised query. These data are provided for data entry and manipulation without having to use the keyboard.
Constants, Names, Language, Globals, Form, Variables, Queries, Settings, Objects are the nine Data Source Types supported in BrightBuilder.
Within the data source tree, an object or methods of an object may contain several icons listed after the node. This signifies that the object or method use is limited to the platforms listed; running them on other platforms will return error codes or will have no effect.
The terminology for these icons are as follows:
| Icon | Operating System |
|
Windows Mobile |
|
Windows Desktop |
|
Android |
|
iOS |
|
Windows Phone |
|
Windows Store App |
|
BrightWeb |
If no icons are listed, the object or method is supported across all platforms. These platform icons may additionally be toggled on/off using the Show Platform Icons option in the Data Source Tree panel.

Constants
Constants are data sources that do not change their value after they have been declared.
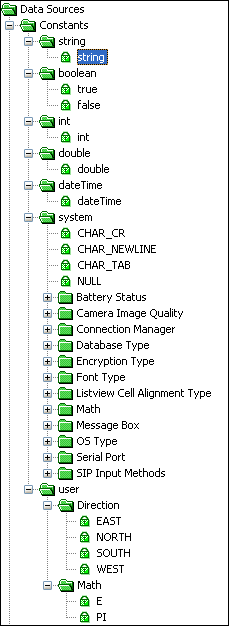
String provides strings, that is, an ordered sequence of characters of essentially arbitrary length. Enclosed in double quotes.
Boolean provides the True or False values.
Int (Integer) provides the numeric data with values between -2147483647 and +2147483647, and zero. No decimal point.
Double provides real numbers, both positive and negative; with values between 1.79769313486231E308 and 4.94065645841247E324.
DateTime provides a means to represent an instant in time, typically expressed as a date and time of day. They may also be operated on as seconds.
System provides a fixed set of values that are used to control various application object methods. One such use is for message boxes, providing constants to the Form.MessageBox method. Sources with the prefix MB, signifies Message Box and defines the message box type that is to be displayed. Sources with the prefix ID refers to the values the message box will return. The System constants that are prefixed with CHAR are string constants for tab, new line and carriage return. The constants prefixed with DB are integer constants equivalent to the database engine that can be used with BrightForms application. And NULL represents the null value that can be used to compare or initialise variables or column fields.
User provides a list of user constants created by the developer in the Globals Element.
The Boolean, System and User constants can simply be dragged and dropped inside the expression, validation rule condition or as parameters. String, DateTime, Int, and Double type constants may be created by double clicking their placeholders in the DST and entering/editing values, then dragging and dropping these nodes into placeholder fields.
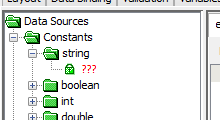
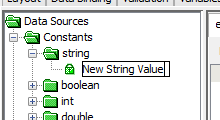
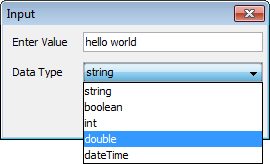
Placeholders within expressions or rules may also be double-clicked to invoke the input dialog as shown below. Values are entered and OK is clicked to populate the placeholder with the type of data selected.
Names
The Names data source provides the tags that are used as parameters for the Methods functions to identify forms, tables, table columns, queries, query output fields and parameters, sync rules and sync rule parameters. These values are enclosed in double quotes to represent a string constant and cannot be assigned any values.
Because BrightBuilder uses drag and drop functionality, the user is spared from the burden of having to memorize the different names for each forms, tables, queries, and sync rules; not to mention the different fields and parameters used in these project elements. Below is an example of an expanded Name Data Source tree.
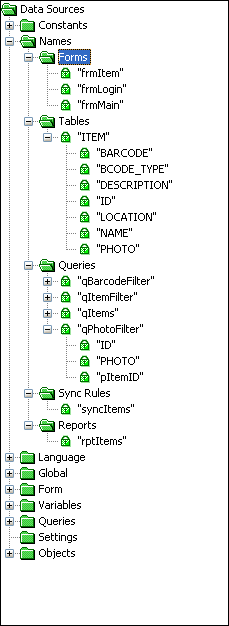
Based from the image above, the project has four forms, three tables, seven queries, no sync rules and no reports.
Language
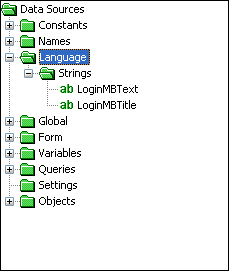
The Language node contains user resource strings for use in the localisation of projects. The following image is an example of the Language Data Source tree.
Global
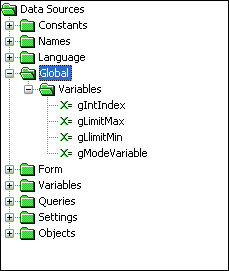
Global data sources contain the global variables available in the project. The following image is an example of the Global Data Source tree.
Form
Form data sources contain the objects required for manipulation of the current form and its child form, including methods for any added controls onto the form. The following is an example of the Form Data Source tree.
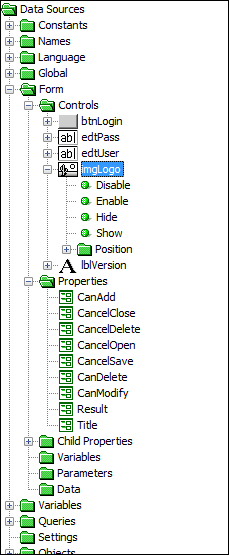
Form data sources are organized into:
Controls - the data held by the form controls. Each control node also contains a set of methods, which may be used to set, retrieve and modify the control via form expressions.
Properties - the form characteristics that can be manipulated by expressions.
CanAdd - allow/disallow new records in a cursor form.
CanDelete - allow/disallow deleting of records in a cursor form.
CanModify - allow/disallow saving changes in a cursor form.
CancelClose - used in Action - Close expressions to cancel the closing of a form.
CancelDelete - used in Action - Pre Delete expressions to cancel the deletion of a record.
CancelOpen - used in a form -Pre Open expression to cancel the opening of a child form.
CancelSave - used in Action - Pre Save expressions to cancel the saving of a record.
Result - an integer return value that can be set within a form and retrieved by a parent form.
Title - set the title of the form window.
Child properties - the child form characteristics that can be manipulated by the form when used only in a pre-open expression or post-close expression.
CanAdd - allow/disallow new records in a cursor form.
CanDelete - allow/disallow deleting of records in a cursor form.
CanModify - allow/disallow saving changes in a cursor form.
HasCursorBar - Set whether the child form is to have a cursor bar.
ReadOnly - allow/disallow write access in child form.
Result - an integer return value that can be set within a form and retrieved by a parent form. This child property is available only in post-close expressions.
Title - set the title of the form window.
Variables - the form variables.
Parameters all the parameters used in the form, can be from a query associated with a listview, combo box, or the form's data binding. Once changed, the values retrieved from the query will only be updated if the control or form itself is refreshed. This is achieved via the Refresh() method for the control or form.
Data - the output of the form's query. There will only be data present if a query is associated with a form under the data binding tab. These data sources may be read from and written to, but will only be saved to the local database when the Form.SaveRecord() object method is called. Other methods to load, change and modify this data is located under the Form > Cursor Form node in the Data Source Tree.
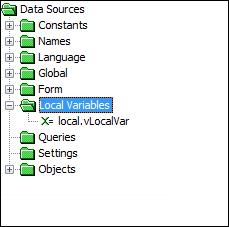
Local Variables
The Local Variables data source allows the creation of local variables that has expression scope.
Local variables may be created in the DST by right clicking the 'Local Variables' node and tapping 'Create New...'. Once created, the values will appear under the node to be dragged and dropped into expressions.
When local variables are double-clicked, they will enter an editing mode which allows users to rename the local variable. Variables renamed will be refactored for their expression. They may also be removed, provided they are unused, by right clicking and selecting 'Remove'.
If using Text Mode, users simply need to type "local.vTempStr" or "local.intTemp" to define a local variable vTempStr and intTemp. Local variables need not be created in the Form Variables.
For more information, please refer to the BrightBuilder > Expressions topic of this document.
Queries
The Queries data source includes the identifiers for all of the parameters, output fields and methods for each query, organised per query name.
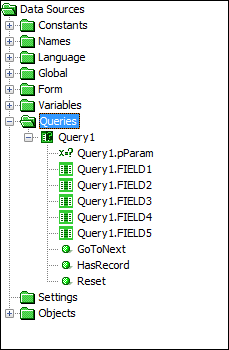
The query parameters can be assigned a value in order to specify query conditions whereas the query outputs are used to yield the values when the query is run. It has the following naming convention: query_name.OUTPUT for query outputs and query_name.ParameterName for query parameters.
Query methods for each query are listed in this node. Once parameters are set, these methods may be used to iterate through the query's result set, with the position in the query and thus output values changing with the GoToNext() method call. Whether or not there are more records in the set may be determined by the HasRecord() method; once there are no more records, HasRecord() will return NULL. The Reset() method will return the position to the first record returned by the query.
Settings
The Settings data source list all the App Settings declared within the project. This allows the user to store data without having to use the database.
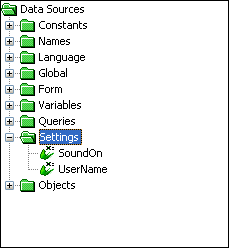
The image above is a sample of the Settings Data Source tree, as shown, there are several settings available in the project.
Objects
The Objects Data Source tree contains methods to manipulate application objects. The arguments of the object methods may be other data sources.
For a complete reference on all the object methods, see the Object Definitions Reference Manual.
The figure below is the Objects Data Source tree with one of the objects expanded, showing that there are several methods available for this object.
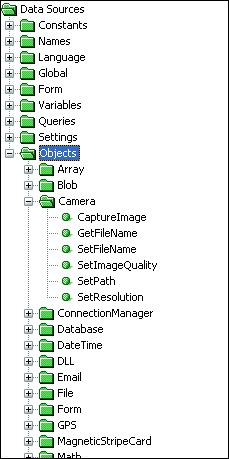
Right clicking on any of the methods and clicking More Info will provide a help message describing the object and its function. While hovering the mouse cursor over an object method will bring up a tool tip.
If the Show Help Window is enabled, once a method is focused, the method information is displayed on the left-bottom section of the expression window.
 When a method has been added in the expression, when the ??? parameter
has been double clicked and it requires a constant value, an Input
Dialog box will appear depending on the parameter i.e Boolean
will display true or false options, Int will display an integer
input dialog. If there is a default value for the method, the
default method parameter value will be automatically inserted.
When a method has been added in the expression, when the ??? parameter
has been double clicked and it requires a constant value, an Input
Dialog box will appear depending on the parameter i.e Boolean
will display true or false options, Int will display an integer
input dialog. If there is a default value for the method, the
default method parameter value will be automatically inserted.
Deprecated Methods
A deprecated method is an object method that is still supported by BrightBuilder and BrightForms, but it is not recommended to use. Usually it would have been replaced by another method. Deprecated methods do not appear in the data source tree but may still be used in valid expressions. A warning will be given upon project validation when a deprecated method has been used.
