Script Methods Reference Manual
Contents Hide
Script Functions
Sync Reader
Sync Reader interface defines how a sync reader interacts with the system. These functions form the contract between BrightServer and a user defined script that provides data to be sent to remote clients or used in the system.

function openReader (query, limit) |
This function is called by the system to prepare the script for data read. The script is expected to prepare itself by opening, connecting or allocating data sources or resources to return data by read() method calls. Parameters: query - String payload. This is the string data that indicates what needs to be read. This will normally be a script query payload sent from the remote device. In addition to a script query payload, advanced SQL and standard query values can be passed. If the remote query is an advanced SQL query, then this string will contain the SELECT statement. If the remote query is a standard query, then this string will contain the query XML. limit - This is specified by the system if the data is to be read in chunks. The unit is the number of records in each chunk. If zero is passed, then this parameter can be ignored.
|
function closeReader () |
This function is called by the system to complete the read operation and close or deallocate any resource that may have been opened or allocated by this script.
|
function read () |
This function is called by the system to read the next set of records from the script. Data must be returned in RecordSet object. Return Values: RecordSet - object that contains data read by the script. Return an empty RecordSet object if no data is available for further read.
|
function dataConsumed () |
This function is called by the system to indicate that the data returned by the previous read() call has been consumed successfully. This can be used to commit any transaction that may have started.
|
Sync Writer
Sync Writer interface defines how a sync writer interacts with the system. These functions form the contract between BrightServer and a user defined script that acts as a data destination in the system. BrightServer will pass the data through this interface. Depending on its current context, the system may ask the script to manage its transaction state through the transaction methods.

function openWriter () |
This function is called by the system to prepare the script for data write. The script is exptected to prepare itself by opening, connecting or allocating data sources or resources to return data by read() method calls.
|
function closeWriter () |
This is called by the system to complete the write operation and close or deallocate any resource that may have been opened or allocated by this script.
|
function write (data) |
This is called by the system to write data. If a data for multiple tables are sent from client (i.e. a sync rule using a multi-table query to send multiple tables records, for example, order headers and order items in a sync rule), then the data input parameter will be a vector of recordsets, containing multiple recordsets each having records from multiple tables sent from client. For a single table write, this data vector will contain just a single recordset containing the records from the table in question. This method may be called multiple times by the system. The transaction status indicated by the beginTransaction, commit and rollback method must be obeyed. Parameters: data - This is a Java Vector of RecordSet objects to consumed. |
function |
This is called by the system to check if the script is in transaction. Return Values: boolean - true if in transaction, otherwise false. |
function
|
This is called by the system to start a transaction to write the data to its destination. Depending upon the destination, this script may opt to start a new transaction at the destination.
|
function commit () |
This is called by the system to commit all data writes within the current transaction that may have been started.
|
function rollback () |
This is called by the system to ask this script to rollback all data written so far within the current transaction that may have been started.
|
Script Job
This interface is designed to run its set of operations repeated over a set period, defined by the server. These scripts may be disabled or enabled, but also be manually run via the Job Status node of BrightServer.
The scripts designed to be run may be included in BrightServer projects, or alternatively defined and uploaded via the BrightServer's Job Configuration.

function run ()
|
This is called by the system when the scheduler triggers the script job as per the schedule defined for the script. |
Online Query
This interface is designed to service to remote online queries generated by remote field devices. A text based string is passed to the execute function to indicate the data requested by the remote user.

function execute (payload)
|
This function is called by the system to source data in a RecordSet object in response to a remote BrightForms client's online query request. The data is prepared by this script depending on the payload data passed. Parameters: payload - String payload. This is the string data that indicates what needs to be returned. This will normally be a script query payload sent from the remote device. In addition to a script query payload, advanced SQL and standard query values can be passed. If the remote query is an advanced SQL query, then this string will contain the SELECT statement. If the remote query is a standard query, then this string will contain the query XML. Return Values: RecordSet - object that contains data returned by the script. |
Remote Procedure Call
This interface is designed to service to remote online queries generated by remote field devices. Remote procedure parameter and parameter values are passed into the script via executeRPC function and resulting RecordSet is sent back to the remote client. The RecordSet object would contain the resulting output field values. With this way, if needed, multiple records can be returned in response to a RPC query. In simple cases where the result is not a recordset, but a collection of output parameters (fields), then the ResultSet object to be returned would contain a single record which in turn would contain the output field values in the expected order.
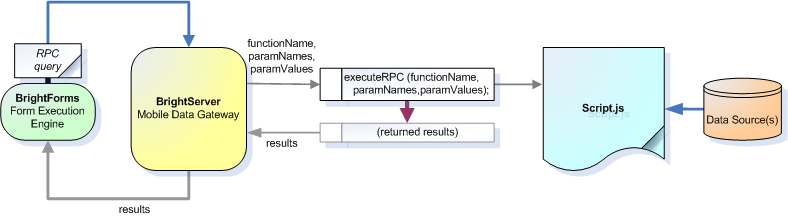
function executeRPC (functionName, paramNames, paramValues)
|
This is called by the system to source data in a RecordSet object in response to a remote BrightForms client's online query request by a RPC (Remote Procedure Call) query. Parameters: functionName - The name of the remote procedure (function) to be executed paramNames - Vector of input parameter names paramValues - Vector of input parameter values Return Values: ResultRPC - RPC result object that contains the data returned by the script. This container object may contain the names and values of the output parameters, or a RecordSet containing records or both depending on the requirements. |
Transform
This is called by the system to transform or manipulate the data sets passed between a data accessor and a client table in the Sync Panel. The transform method can be used to perform complex operations to data sets, from either client to server or server to client. To apply transformations, simply expand a client table sync point, and tap on the 'T' icon, or select an existing transformation script via the node's properties panel.

For more simple remapping or renaming of fields, the codeless, simple Mapping should be considered.

function transform (data)
|
This is called by the system for script to transform or manipulate the data passed. Parameters: data - This is a Java Vector of RecordSet objects to transformed. |
Script Types
Specifies a run script to execute on server event.


function run () |
This is called by the system based on the Script Type; either after login/logout, or server start/shutdown.
|
function authenticate (name, password) |
This is called by the system when a user logs in to BrightServer and determines whether the given username and password is valid. A user is considered to have logged in each time they attempt to synchronise, logs into the BrightBuilder Server Management Console or the BrightServer browser based Management Console. Parameters: name - The username provided by the user. password - The password provided by the user. Return Values: return - Boolean return object; true if user authentication passes, otherwise false. |
WebService
This interface is designed to handle SOAP requests to BrightServer via web service calls.
SOAP requests and responses are deserialised internally via the WebMessage object. This enables developers to analyse and construct SOAP communications, while not needing any specific parsing.
For more information, please refer to the BrightServer > Web Services chapter of this documentation.

function handle (request)
|
This is called by the system in response to a remote web services call. It accepts a WebMessage representing the SOAP message received. It must return a WebMessage object representing the web services call result. Parameters: request - A WebMessage object representing the request. Return Values: return - A WebMessage object representing web services call response. |
Helper Objects
Blob
JavaScript does not provide support for binary data and does not have a byte data type. This object is a helper function to address this. Using Blob object and its provided functionality blobs can be processed and created by scripts.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.Blob) ;
Blob () |
Creates a new empty blob object. Return Values: Blob - new blob object |
Blob (byte[] data) |
Creates a new blob with the contents 'data'. Parameters: data - data represented as a binary array Return Values: Blob - blob containing specified data |
int getLength () |
Returns the length of a particular blob, in bytes Return Values: int - integer value specifying blob's length |
byte[] getBytes () |
Returns a blob as a byte array. Return Values: byte[] - byte array representation of the blob |
void readFromFile (String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException |
Read file contents into a blob. Parameters: fileName - full path and name of the file. |
void writeToFile (String fileName) throws IntegratorException |
Write contents of a blob into a file. Parameters: fileName - full path and name of the file. |
void compress () throws IntegratorException |
Compresses data within a blob.
|
void decompress () throws IntegratorException |
Decompresses data within a
blob.
|
Dropbox
Script object to manage Dropbox integration. To use this, an app configuration must exist under the dropbox developer account, with a valid oauth token. Applications may be configured to access specific folders, or the entire dropbox directory.
The dropbox object is created by using the ScriptSession.createDropboxObject() method with dropbox token, retrieved from the Dropbox website. For more information on retrieving the dropbox token, please refer to the Generating Dropbox Access Token section in the Appendix.
Once retrieved, the token may be used to instantiate, then access the object. For example:
var token = "<YOUR-ACCESS-TOKEN>";
try
{
var dropbox = ScriptSession.createDropboxObject(token) ;
ScriptSession.logInfo("Getting account details...") ;
ScriptSession.logInfo("Account Id = " + dropbox.getId()) ;
ScriptSession.logInfo("Account Name = " + dropbox.getName()) ;
ScriptSession.logInfo("Account Surname = " + dropbox.getSurname()) ;
ScriptSession.logInfo("Account Display Name = " + dropbox.getDisplayName()) ;
ScriptSession.logInfo("Account Disabled = " + dropbox.isDisabled()) ;
ScriptSession.logInfo("Account Type = " + dropbox.getAccountType()) ;
ScriptSession.logInfo("Account Email = " + dropbox.getEmail()) ;
}
catch (error)
{
...
}
Unless specified, all methods may throw DbxException on error, and should thus be surrounded by try-catch statements.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.Dropbox) ;
String getId () |
Returns the id of the account connected to. Return Values: String - Id of the account connected |
||||||||
String getName () |
Returns the name of the account connected to. Return Values: String - Name of the account connected |
||||||||
String getSurname () |
Returns the surname of the account connected to. Return Values: String - Surname of the account connected |
||||||||
String |
Returns the display name of the account connected to. Return Values: String - Display name of the account connected |
||||||||
boolean isDisabled () |
Checks if the account is disabled. Return Values: boolean - true if disabled, otherwise false |
||||||||
int |
Returns the name of the account connected to. Return Values: int - Name of the account connected
|
||||||||
String getEmail () |
Returns the email of the account connected to. Return Values: String - Email of the account connected |
||||||||
String[] getFileListEmail (String dropboxPath) |
Returns the list of files at the path specified. Parameters: dropboxPath - Path to be listed Return Values: String[] - File or folder names at the specified path |
||||||||
DropboxMetadata getMetadata (String name) |
Returns the metadata for the entry specified Parameters: name - File with full Dropbox path or folder name Return Values: DropboxMetadata - Metadata object describing the entity details |
||||||||
boolean exists (String name) |
Checks if the file or the folder specified exists on Dropbox. Parameters: name - File or folder name to be checked Return Values: boolean - true if the file exists, otherwise false |
||||||||
void uploadFile (String source, String destination, boolean bOverwrite) throws FileNotFoundException, DbxException, UploadErrorException, IOException |
Read file contents into a blob. Parameters: source - Source file name at the current machine destination - Dropbox file path and name |
||||||||
void downloadFile (String source, String destination) throws FileNotFoundException, DbxException, UploadErrorException, IOException |
Write contents of a blob into a file. Parameters: source - Dropbox file path and name destination - Local destination file name |
||||||||
void copy (String source, String destination, boolean bAutoRename) |
Copies a file/folder in Dropbox to another file/folder in Dropbox. Parameters: source - Source name destination - Destination name bAutoRename - If there's a conflict, have the Dropbox server try to auto-rename the file to avoid the conflict. |
||||||||
void move (String source, String destination, boolean bAutoRename) |
Moves a file/folder in Dropbox to another file/folder in Dropbox. Parameters: source - Source name destination - Destination name bAutoRename - If there's a conflict, have the Dropbox server try to auto-rename the file to avoid the conflict. |
||||||||
void delete (String name) |
Deletes a file/folder from Dropbox. Parameters: name - Entity to be deleted |
DropboxMetadata
This is the helper object for returning a Dropbox metadata object.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.DropboxMetadata) ;
String getId () |
Returns a unique Dropbox identifier for the file or the folder. Return Values: String - Unique Dropbox identifier for the file |
String getName () |
Checks if the entity is a file. Return Values: boolean - true if it is a file, otherwise false |
boolean isFile () |
Client modification date of the file. Return Values: boolean - true if it is a folder, otherwise false |
boolean isFolder () |
Returns the display name of the account connected to. Return Values: String - Display name of the account connected |
Date |
For files, this is the modification time set by the desktop client when the file was added to Dropbox. Since this time is not verified (the Dropbox server stores whatever the desktop client sends up), this should only be used for display purposes (such as sorting) and not, for example, to determine if a file has changed or not. Return Values: Date - Client modification date of the file |
Date |
Returns the last time the file was modified on Dropbox. Return Values: int - The last time the file was modified on Dropbox, null if not a file |
long getFileSize () |
Returns the file size in bytes. Return Values: long - File size in bytes or -1 if not a file |
String getRevision () |
Returns a unique identifier for the current revision of a file. Return Values: String - File revision or an empty string if not a file |
Email object is a helper object to send messages in scripts..
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.Email) ;
Email (String host, String port, String from, String to) |
Creates a new Email object to send email messages to specified destination email addresses. Parameters: host - Outgoing mail server address port - Outgoing mail server port number (generally use the default port 25) from - Email address that the message is sent from (i.e. source email address) to - Email address that the message is sent to (i.e. destination email address) |
void setSubject (String subject) |
Sets the message subject. Parameters: subject - Subject text of the message to be sent |
| void
setBody (String messageBodyText) |
Sets the message text. Parameters: messageBodyText - The text for the message body |
| void
setText (String subject, String messageBodyText) |
Sets the subject and the body text of the message to be sent in a single method call. This is equivalent to calling setSubject and setBody method in separate calls. Parameters: subject - Subject text of the message to be sent messageBodyText - The text for the message body |
| void
setFromName (String fromName) |
Sets the human readable sender name for the message. Parameters: fromName - String to display for email sender address |
| void
setUserCredentials (String userName, String userPassword) |
Sets the username and password credentials for outgoing mail server authentication. Parameters: userName - Outgoing mail server user name userPassword - Outgoing mail server user password |
| void
setEnableSSL (boolean bIsEnabled) |
Enables or disables the SSL option when sending mails. By default the SSL option is turned off. Parameters: bIsEnabled - true to enable the SSL option, false to disable it By default the SSL option is set to false. Use this method to turn it on or off. |
| void
setProtocol (String protocol) |
Sets the mail protocol type to be used. Parameters: protocol - Mail protocol name other than the default "smtp" protocol being used. By default the "smtp" protocol is used. The valid options are "smtp", "pop3" or "imap". An incorrect option will be ignored by this method. |
| void
setProperty (String propertyName, String propertyValue) |
Sets the named mail object property value. Parameters: propertyName - Mail property name propertyValue - Mail property value as string This is a reserved method to set mail object properties as recommended by the support team. |
| void
addAttachment (String fileName) |
Attaches the content of the specified file to the message to be sent. Parameters: fileName - Name of the file to be attached to the message |
| void
addBCC (String address) |
Adds the email address to the BCC list of the message to be sent. A copy of the message will also be sent to this email address, not visible to other addresses. Parameters: address - Email address to which the message is also be sent in addition main receiver. |
| void
addCC (String address) |
Adds the email address to the CC list of the message to be sent. A copy of the message will also be sent to this email address. Parameters: address - Email address to which the message is also be sent in addition main receiver. |
| void
addTo (String address) |
Adds the email address to the To list of the message to be sent. A copy of the message will also be sent to this email address. Parameters: address - Email address to which the message is also be sent in addition main receiver. |
| void
send () |
Send the message to its destination and the email addresses in the CC list.
|
GCMService
GCMService created by ScriptSession.createGCMServiceObject(), and is used to push messages to devices via Google Cloud Messaging service as an alternative to static IP pushing with the Push() object.
For more information, please refer to BrightServer > Script Push > Pushing to Cloud Services in this document.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.GCMService) ;
void setMessagePriority (String priority) |
Sets the message priority. The current valid values are "high" and "normal". Refer to Google documentation for any changes. Parameters: priority - Message priority |
void setTestMode (boolean bInTestMode) |
Sets the test mode. When set to true, allows developers to test a request without actually sending a message. Parameters: bInTestMode - true if the test mode is on |
void setDataValue (String key, Object value) |
Sets the key/value pairs in the "data" section. Parameters: key - Key name value - Key Value |
void setNotificationValue (String key, Object value) |
Sets the key/value pairs in the "notification" section. Parameters: key - Key name value - Key Value |
void setMessageParameter (String key, Object value) |
Sets the named message parameter values. This method is in addition to the other object methods provided such setTimeToLive, setMessagePriority etc. This is provided so that we can continue server GCM API changes in the future. The values set by this method will be applied last, just before the message is to be transmitted to the GCM server. Parameters: key - Key name value - Key Value |
void |
Clears the data and notification values set previously to create and send a new message to the GCM service. |
void sendMessageToDevice (String recipient, String text) throws IntegratorException |
Sends the composed message to the recipient specified. Parameters: recipient - Unique identifier of the device registered with the GCM service collapseKey - This parameter identifies a group of messages (e.g., with collapse_key: "Updates Available") that can be collapsed, so that only the last message gets sent when delivery can be resumed. This is intended to avoid sending too many of the same messages when the device comes back online or becomes active (see delay_while_idle). Note that there is no guarantee of the order in which messages get sent. Note: A maximum of 4 different collapse keys is allowed at any given time. This means a GCM connection server can simultaneously store 4 different send-to-sync messages per client application. If you exceed this number, there is no guarantee which 4 collapse keys the GCM connection server will keep. |
void sendMessageToUser (String userName, String text) throws IntegratorException |
Sends the composed message to the user specified. Parameters: userName - BrightServer username to receive the message collapseKey - See above |
void sendTextMessageToDevice (String recipient, String text, String collapseKey) throws IntegratorException |
Sends a simple text message to the device with the registration token. Parameters: recipient - Unique identifier of the device registered with the GCM service text - Text message collapseKey - See above |
void sendTextMessageToUser (String userName, String text, String collapseKey) throws IntegratorException |
Sends a simple text message to the user specified. Parameters: userName - BrightServer username to receive the message text - Text message collapseKey - See above |
void sendNotificationToDevice (String recipient, String title, String text, String collapseKey) throws IntegratorException |
Sends a notification message to the device with the registration token. Parameters: recipient - Unique identifier of the device registered with the GCM service title - Pop-up title text - Text message to be sent collapseKey - See above |
void sendNotificationToUser (String userName, String title, String text, String collapseKey) throws IntegratorException |
Sends a notification text to the user specified. Parameters: userName - BrightServer username to receive the message title - Pop-up title text - Text message to be sent collapseKey - See above |
String getGCMTokenForUser (String userName) throws IntegratorException |
Returns the GCM token for the user specified. Parameters: String - username Return Values: String - Registered GCM token that is used by the user device. |
Push
Push object enables server side scripts to package and send data to remote devices in the field in an unsolicited fashion without the need for them to poll server for a new data. Remote devices in this context are referenced as remote servers running BrightForms Mobile Device Engine. BrightForms application running on remote devices is expected to have been configured to listen to the push messages sent from BrightServer on the configured TCP/IP port. Push object enables script writers to package data and push to remote devices (full push) or force them to synchronize data by getting them to execute the specified sync rules in the background (semi push).
For more information, please refer to the Script Push section of this document.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.Push) ;
Push (String remoteServerAddress, int portNumber) |
Creates a new Push object to send data to a remote device defined by its address and port number. Parameters: remoteServerAddress - Remote device's IP address portNumber - Port number |
void sendData (Vector data) |
Sends unsolicited data to a remote device. Parameters: data - Vector of script RecordSet objects to be sent to remote device |
| void
forceRemoteSync (String syncRuleNames) |
Forces remote client to execute the specified sync rules. This will be a comma separated sync rule names. Return Values: syncRuleNames - Comma separated sync rule names to be executed by the remote device |
Report
Report is instantiated by ScriptSession.createReportObject(), and configured to print a named report contained in the BEP.
For more information, please refer to BrightServer > Report Generation.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.Report) ;
close ()
|
Closes the object by releasing application resources. This must be called by the user when finished using the object. |
void setDataSource (String source) |
Sets the server data source that the report data is to be fetched from. Parameters: source - String representing the data source in the following format: <SyncPointName>_<DatabaseNodeName> SyncPointName is the name of the sync point in the BEP project where the database node has been placed and named as DatabaseNodeName. |
void setVariable (String name, Object value) |
Sets the named report variable value. Parameters: name - Name of the report variable value - New value of the report variable |
void setQueryParam (String name, Object value) |
Sets the named report query parameter value. Parameters: name - Name of the parameter to be set value - New value of the parameter |
void setPageSize (int widthInMM, int heightInMM) |
Sets the printable PDF page size in millimeters. Parameters: widthInMM - Width in millimeters heightInMM - Height in millimeters |
int printToPDF (String reportName, String fileName) |
Prints the named report to the file specified. Parameters: reportName - Name of the report to be printed fileName - Name of the PDF file to be created return - ObjectError.BS_SUCCESS on success, otherwise the error code |
Util
This is a utility object that provides functionality to encode or decode Base64 data if required in your script.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.Util) ;
void copyFile (String source, String destination) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException |
Copies the source file to the destination file. Parameters: source - Source file name including the full file path destination - Destination file name including full path |
void convertCSVToExcel (String sourceCSVFileName, String destinationExcelFileName, String destinationSheetName) throws IOException, Exception |
Converts the source CSV (Comma Separated Values) file to a Microsoft Excel file. Parameters: sourceCSVFileName - Source CSV file name including the full file path destinationExcelFileName - Destination CSV file name including the full path destinationSheetName - The name of the destination sheet that will contain the CSV data |
void convertExcelToCSV (String sourceExcelFileName, String sourceSheetName, String destinationPath, boolean bIgnoreFirstLine, String strColumnMap) IOException, SAXException, OpenXML4JException, InvalidFormatException, ParserConfigurationException |
Converts the source Microsoft Excel file to a CSV (Comma Separated Values) file. Parameters: sourceExcelFileName - Source Excel file name including the full file path sourceSheetName - The name of the source sheet in the Excel file of which content will be converted to a CSV file (e.g. 'Sheet1') destinationPath - Destination path (i.e. the directory name) in which the CSV file is to be created with the same name of the source Excel file with the .CSV extension. bIgnoreFirstLine - Whether first line of the Excel file is to be ignored or not. This may be useful if the first header row is not required to be in the output CSV file strColumnMap - Column order referring to the columns of the Excel file as they will appear in the CSV file. It is a comma separated list of column indexes. Using this argument, desired rows can be omitted from the output CSV file. Use null if the original column order is to be preserved. |
String encodeBase64 (byte[] value) |
Converts an array of bytes into a base64binary string. Parameters: value - binary byte array Return Values: String - base64 string value |
byte[] decodeBase64 (String value) |
Converts a base64binary into an array of bytes. Parameters: value - base64 string value Return Values: byte[] - binary byte array |
Vector groupData (Vector data, Vector relationships) |
Groups the user data and returns the grouped data in a vector of ResultSet objects. Parameters: data - User data to be grouped. This is a vector of ResultSet objects relationships - This is a vector of vectors which are the relationships. A relationship vector MUST contain four elements in the following order: 1) Name of the parent set (i.e. the name of the parent ResultSet) 2) Name of the child set (i.e. the name of the child ResultSet) 3) Vector of the names of the fields of the parent set for the grouping to occur over. 4) Vector of the names of the field of the child set for the grouping to occur over, matching the order of those defined in (3). This method uses the relationship fields and groups the child records headed by the parent records. More than one relationship can be defined for grouping multiple related sets. Return Values: Vector - A vector of a vector of ResultSet objects containing grouped data. |
String readFile (String fileName) FileNotFoundException, IOException |
Reads the content of the named file and returns it as a String. Parameters: fileName - Name of the file to be read, including the full file path. |
Vector split (String input, String token) |
Returns a vector of strings by splitting (tokenizing) the input string by using the special delimiter string (e.g. a comma character). Parameters: input - String to be tokenized. token - Tokenizer String (e.g."',") |
Vector splitCSVString (String input) |
Parses a Comma Separated Values (CSV) string and returns a vector of strings Parameters: input - A CSV string to be parsed |
void writeFile (String fileName, Object value, boolean bAppend) IOException |
Writes the object value to the file specified. Parameters: fileName - Name of the file to be written to, including the full file path. value - Value to be written. The value could be a String or a byte array for creating binary files. bAppend - true to append to the content of the file if it exists, false to overwrite its content. |
ScriptSession
ScriptSession is a script variable created and managed by the system. They are passed into the current script being executed as a global script variable. It provides the information about the current runtime environment as well as passing back data to it such as error information. It provides the necessary methods to create system log entries in debug, info and error levels. importClass or importPackage statements are not required to use this object.
Import Statement : Not required.
GCMService |
Creates and returns a new GCMService object to be used in scripts. Return Values: GCMService - Newly created GCMService object |
Dropbox createDropboxObject (String token) |
Creates a Dropbox object for accessing Dropbox from scripts. Parameters: token - Dropbox access token Return Values: Dropbox - Newly created Dropbox object, null on error |
JobManager |
Creates a JobManager object for managing and running user defined jobs. See Job Processor Object for more details. Return Values: Report - Newly created JobManager object |
Report |
Creates a Report object for creating PDF reports from scripts. Return Values: Report - Newly created Report object |
String getUserName () |
Returns the username of the user who instantiated the script, corresponding to BrightForms' settings. Return Values: String - user name in string format |
String getLastError () |
Returns last recorded error message in string format, as recorded by the setError() method. Return Values: String - error message in string format. |
| int
getLastErrorCode () |
Returns last recorded error code, as recorded by the setErrorr() method. Return Values: int - error code as an int |
void setError (int code, String desc) |
Stores an error code and error message. Parameters: code - error code as an int desc - error message in string format. |
Connection |
Returns a Java JDBC database connection to the internal memory database. |
Connection |
Returns a Java JDBC database connection to the default system database. If not configured specifically, it will be the default internal brightdb database. |
| boolean
isDebugLogEnabled () |
Checks if debug messages are enabled on the BrightServer instance. This can be used to prevent the unnecessary string manipulation as it can be costly to create and manipulate strings. Return Values: boolean - true if the trace level is set to DEBUG in hte BrightServer instance. |
| boolean
isInfoLogEnabled () |
Checks if info messages are enabled on the BrightServer instance. This can be used to prevent the unnecessary string manipulation as it can be costly to create and manipulate strings. Return Values: boolean - true if the trace level is set to INFO in the BrightServer instance. |
| void
logDebug (String message) |
Logs a "debug" level message to the BrightServer log file. This method creates a log entry only if the trace level is set to "debug", "info", or "warning". This is controlled by the log4j.xml in the "conf" subdirectory where the server is installed. Parameters: message - string message to be logged |
| void
logInfo (String message) |
Logs an "info" level message to the BrightServer log file. This method creates a log entry only if the trace level is set to "debug" or "info". This is controlled by the log4j.xml in the "conf" subdirectory where the server is installed. Parameters: message - string message to be logged |
| void
logWarn (String message) |
Logs a "warning" level message to the BrightServer log file. This method creates a log entry only if the trace level is set to "debug" or "info" or "warning". This is controlled by the log4j.xml in the "conf" subdirectory where the server is installed. Parameters: message - string message to be logged |
| void
logError (String message) |
Logs an "error" level message to the BrightServer log file. This method creates a log entry only if the trace level is set to "error". This is controlled by the log4j.xml in the "conf" subdirectory where the server is installed. Parameters: message - string message to be logged |
| void setVariable (String name, Object value) |
Saves the script variable value in the system for later retrieval. The value of the script parameter will be available between the invocations of scripts. However the values will be lost between the starts of BrightServer. This means they are saved in memory (RAM) only. If you need to store the values permanently then use the persistVariable method. Parameters: name - Name of the variable to be stored value - Value of the script variable. This is a Java object. JavaScript natives data type are converted to Java objects |
| void
persistVariable (String name, Object value) |
Saves the script variable value in the system for later retrieval. The value of the script parameter will be persisted permanently by the system and will be available between the starts of BrightServer, but limited to the server configuration deployment. If variables do not need to be persisted between BrightServer restarts, the setVariable method should be used. Parameters: name - Name of the variable to be stored. The variable will be persisted permanently to the server's runtime database. value - Value of the script variable. This is a Java object. JavaScript natives data type are converted to Java objects |
| Object
getVariable (String name) |
Returns the value of the specified variable. If the value cannot be found than, a NULL will be returned. Parameters: name - Name of the variable to be returned as a Java object. |
| void
persistUniversalVariable (String name, Object value) |
Saves the script variable value in the system for later retrieval. The value of the script parameter will be persisted permanently by the system and will be available between the starts of BrightServer for all scripts. Use persistVariable for globally stored variables within scripts. Parameters: name - Name of the variable to be stored. The variable will be persisted permanently to the server's runtime database. value - Value of the script variable. This is a Java object. JavaScript natives data type are converted to Java objects |
| Object
getUniversalVariable (String name) |
Returns the value of the specified universal variable. If the value cannot be found than, a NULL will be returned. Parameters: name - Name of the variable to be returned as a Java object. |
| String
getUserRemoteHostAddress () |
Returns the raw IP address of the remote device in a string format. This method can be used to detect the IP address of the user connecting server for the purposes of identifying the user device on the network for unsolicited push messages by using the Push script object.
|
| int
getSystemVersion () |
Returns BrightServer version. If the BrightServer version is 1.2.3, then it will return 10203. That is, the major version is multiplied by 10000, and the minor version is multiplied by 100 and then they are simply added to the third bug fix version number. Similarly for Version 5.2.0, it will return 50200; and for Version 6.0.5, it will return 60005; and so on. This method can be used to differentiate the server versions when upgrading scripts to ensure backwards compatibility. |
| String
getConfigProperty (String propertyName) |
Returns the named property value from a user defined properties file, uploaded to BrightServer with BEP on deployment. A properties file is a file containing a number name-value pairs which may be used to configure server details without modifying the server logic of the project. This file is typically uploaded to the server with the BEP definition. For more information, refer to the BrightServer > Configuration Property Files chapter of this document. Parameters: propertyName - Name of the property to be read from the property file deployed |
| String
getConfigFileProperty (String fileName, String propertyName) |
Returns the named property value from a user defined properties file, which exists as a file on the file system, independent of those uploaded to the server with project deployments. Typically, this method would only be used over getConfigProperty for backwards compatibility purposes. Parameters: fileName - Name of the property file that is holding the property name-value pairs. This must include full path name as well. propertyName - Name of the property to be read from the property file |
| void
startLogging (String fileName) |
Start capturing log entries into the named log file until stopLogging method is called. Parameters: fileName - Log file name including the full path name. |
| void
stopLogging () |
Stops the capture of the log entries started by the startLogging method.
|
SystemConfiguration
This is a helper object to configure runtime objects.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.SystemConfiguration) ;
| boolean
userExists (String userName) |
Returns whether or not the user exists in the system. Parameters: userName - Username to check Return Values: boolean - true if the user exists, false if they do not |
User createUserObject (String userName) |
Creates a user object to be used to manage the user account. If there is already a user in the system with the name specified name, then its details will be loaded into the object returned. If the user does not exist, then a new User object will be returned. Parameters: userName - Username to load/create Return Values: User - User object representing either a new user, or an existing user |
String[] getUserList () |
Returns an array of user names currently on BrightServer Return Values: String[] - Array of usernames |
User
This object is a Helper object for managing runtime user configuration.
The object is created by SystemConfiguration.createUserObject(), then methods are called to modify the user account on the server.
For example:
var user = SystemConfiguration.createUserObject("exampleUser");
if (user.isActive())
{
user.deactivate();
}
user.update();
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.User) ;
String getName ()
|
Returns the user name. Return Values: String - Username |
boolean isActive () |
Checks if the user account is active (enabled) or not. Return Values: boolean - true if the user account is active, otherwise false |
void setPassword (String password) |
Sets the user password. Parameters: password - New user password |
void activate () |
Activates the user account. |
void deactivate () |
Deactivates the user account. The user will no longer be able to access server. |
void |
Enables the user account to access BrightWeb. |
void |
Disables BrightWeb web access. |
void setGroup (String groupName) |
Updates the group that the user belongs to. Parameters: groupName - Group name |
void setApplication (String appName, int appVersion) |
Updates the group that the user belongs to. Parameters: appName - Project name appVersion - Project release number |
void setServerConfiguration (String configName, int configVersion) |
Updates the group that the user belongs to. Parameters: configName - Server configuration name configVersion - Server configuration version |
| boolean
create () |
Creates a new user account in the system. Return Values: boolean - true on success, false on failure |
| boolean
update () |
Updates the user account in the system. Return Values: boolean - true on success, false on failure |
| boolean
delete () |
Deletes the user account from the system. Return Values: boolean - true on success, false on failure |
Data Objects
RecordSet
The RecordSet object represents a vector of records. It is the container of records object. Every RecordSet object has a name and it contains a meta data as to what sort of fields or values exist in every record. This is analogous to the database table definition. In short, this FieldInfo data describes the data contained in the RecordSet. RecordSet objects are used in conjunction of Record object when producing or consuming data.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.RecordSet) ;
RecordSet (String name) |
Creates a new empty record set with a given name, without field information. Please note that when consuming records, if no field information is present, an exception will occur on the server. Parameters: name - name of the new record set. The name is important for sync queries, and must match tables defined on the server. Return Values: RecordSet - empty record set with no field data. |
RecordSet (String name, Vector vectFeldDefs) |
Creates a new empty record set with a given name, and with given field parameters. Parameters: name - name of the new record set. The name is important for sync queries, and must match those defined in the server. vectFieldDefs - a vector of FieldInfo which defines what the values in each field of the record set consecutively. Return Values: RecordSet - empty record set with defined field types. |
String getName () |
Returns the name of a record set. Return Values: String - the name of a recordSet |
Vector getFieldInfo () |
Returns the type data for the fields (columns) in a data set. Return Values: Vector - an array of FieldInfo which defines what the values in each field of the record set consecutively. |
void setFieldInfo (Vector vectFieldInfo) |
Defines the field parameters for a RecordSet. Parameters: Vector - a vector of FieldInfo which defines what the values in each field of the record set consecutively. |
void addRecord (Record record) |
Add a record (row) to a given RecordSet. Parameters: Record - a record which is to be added to the record set. |
Record get (int index) |
Get a particular row in a record set, given it's index - similar to row number. Parameters: index - index of the desired record. Return Valuess: Record - the record at the specified index. |
boolean isEmpty () |
Check if a RecordSet contains no records Return Values: boolean - true if the RecordSet is empty. |
int size() |
Returns the size of a record set, with regards to how many records it is currently holding. Return Values: int - number of records in the record set |
Record
This object represents a collection of values. This is analogues to a database table record. Values in a record can be of different data types including numeric, string, datetime and binary data etc. Record objects would be used when writing sync source or sync destination scripts to process the data received from the field or send back the data read from other data sources A Record object has a state concept to indicate whether it is a newly created object, or modified one or deleted. When implementing sync destination using Sync Writer interface, the status of the record must be checked to see what action needs to be taken by the script. If a record is deleted from the remote device, then its status will be marked as deleted and the script will need to delete the record from the sync destination.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.Record) ;
Record () |
Creates an empty record (row), with status unknown. Return Values: Record - an empty set of records marked with status. |
|||||||||||||||
Record (int status) |
Creates an empty record with the specified status. Parameters: status - the status of the record as an int.
Parameters: Record - an empty set of records marked with status. |
|||||||||||||||
Record (int status, Vector data) |
Creates a record with a status and a set of predefined data Parameters: status - the status of the record as an int.
data - a vector of object data to store in the record Return Values Record - an empty set of records marked with status. |
|||||||||||||||
int getStatus () |
Returns the status of a record. Return Values int - the int value describing status.
|
|||||||||||||||
Vector getAsVector () |
Returns the record as a vector of objects. Return Values Vector - vector of objects; standard vector operations apply. |
|||||||||||||||
Object get (int index) |
Returns an the object at the index specified, analogous to a column number if a record is seen as a row. Parameters: index - the position of the object in the record Return Values Object - object at the index specified |
|||||||||||||||
void add (Object value) |
Append an object to the record vector. Parameters: value - the object which is to be appended. |
|||||||||||||||
void set (int index, Object value) |
Set an object to the record vector, at a particular index. Parameters: index - index which the object will populate value - value to place in the record set. |
|||||||||||||||
void remove (int index) |
Removes a particular object at a given index from the vector. Parameters: index - index at which the object is removed. |
|||||||||||||||
boolean isEmpty () |
Returns true if a record is empty, false if not. Return Values: boolean - true if record is empty. |
|||||||||||||||
int size () |
Returns the size of a record, with regards to how many fields it is currently holding. Return Values: int - number of fields in the record |
FieldInfo
FieldInfo describes the meta data of a record field. Every RecordSet object contains a collection of FieldInfo object to describe its data. FieldInfo contains the field's name, its data type, if the field is a primary key field or not, the length of the field if it is a string field, and if the field can contain null values of not).
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.FieldInfo) ;
FieldInfo (String name, int type, boolean isPK, int len, boolean isNullable) |
Create a new FieldInfo construct that may be used to define the 'columns' in a given record set. It is important that this information matches those mapped in a BrightServer instance upon synchronisation. Parameters: name - the name of the 'column' type - value type of an object
isPK - true if the field contains the record's primary key len - the max length of the Field if it is a string value (ie, type = 1) isNullable - set to true if the field value may be NULL Return Types: FieldInfo - return a FieldInfo object to be used with the RecordSt class, which defines the fields given a column in a record set. |
||||||||||||||||
String getName () |
Sets the name of the field to be defined. Corresponds to 'column name' in a table definition. Return Types: String - returns the name of the string to which the FieldInfo object refers to. |
||||||||||||||||
int getType () |
Get the object type of the field. Return Types: int - returns the type value the field is set to. |
||||||||||||||||
boolean isPK () |
Returns true if the field is a primary key, false if not. Return Types: boolean - true if the field is a primary key. |
||||||||||||||||
int getLength () |
Returns the length of the field. Applicable for strings. If the field is not a string type, 0 may be entered. Return Types: int - the length of the field if it is of type 1 (string), otherwise 0. |
||||||||||||||||
boolean isNullable () |
Returns whether the field is nullable or not. Return Types: boolean - true if the field may be set to NULL |
ResultRPC
ResultRPC object represents a RPC result. A RPC call may return a number of output parameter values, or a recordset, or both depending upon the requirements for the RPC query sent from the remote field device. This object is simply a container object for holding the returned values. It allows setting the returned output parameter name and value pairs. It also allows returning a RecordSet object for returning records in the RPC result object. A ResultRPC object also holds a query result integer value. An error code can be returned by setting the result code as well.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.ResultRPC) ;
ResultRPC()
|
Creates a new ResultRPC container object. The result code is set to 0 by default. |
void setOutputParameter (String name, Object value) |
Puts a name value pair into the RPC result object as an output parameter value. This name-value pair will be returned in back to the remote client in the result output parameter list defined by the query. Parameter must be defined by the query as an output parameter. Important to note that parameter names are case sensitive. Parameters: : name - Case sensitive parameter name value - Parameter value as a Java object |
void setRecordSet (RecordSet rs) |
Puts a recordset object into the RPC result object. Parameters: : rs - ResultSet object containing record(s) |
void setResultCode (int err) |
Returns an error code by setting the result code. When a ResultRPC object is created, the result code is set to 0 assuming no error has occurred. Use this method to change an error code if needed to indicate an error condition occurred. Parameters: : err - RPC call result code |
WebMessage
WebMessage object represents a web services message received from a remote caller, as well is used to construct web services responses to be sent to remote callers. It is the object that abstract the web services layer des-serialization of the messages received and serialization of the web services responses prepared by the user scripts to be sent to the caller. Every WebMessage has a name to reflect the Web Services message, and a collection of named parameters of the web services message received. The web service message name is naturally a String. However message parameters can be of any Java data type including simple data types such as String, Integer Java objects. Depending on the protocol designed, a parameter can also be of type of Java Vector for instance. Similarly the response to be sent to the caller can contain simple data types as well as complex Java objects vectors, maps etc.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.WebMessage) ;
void createMessage (String messageName) |
Prepares the object for a new web services message to be sent to the caller as the response. Parameters: : messageName - SOAP message method name to be used to create the message |
void decode (byte[] message) |
Populates the WebMessage's message name and parameters based off input byte data. Parameters: : message - Byte array containing the message to be converted. |
String build () |
Returns the XML string value of the WebMessage. Return Values: String - String value of the webmessage |
void addParam (String paramName, Object paramValue) |
Adds a new parameter to the message created. Parameters: : paramName - Name of the parameter paramValue - Value of the parameter. This can be of a simple data type, such as Integer, String etc. Or it can be a Java container object such a Vector. It is up to the web services protocol to define the layout of the response parameters. |
String |
Returns the name of the SOAP method of the web services call received. This could be useful if the script is expecting multi message types to process Return Values: String - Method name of the web services call received. |
Object getParam (String paramName) |
Returns the parameter value of the web services call received. Parameters: : paramName - Name of the parameter Return Values: Object - Parameter value. This can be of a simple data type such as Integer, String etc., or can be a Java container object such a Vector. It is up to the web services protocol to define the layout of the input parameters. |
Job Processor Objects
This API set exposes the built-in job processor sub-system functionality to the developers for easily creating integration tasks in order to exploit the built-in capabilities that is shipped by BrightServer. Historically BrightServer has been shipping with the Job Processor that was the integral building block of the now defunct product called BrightIntegrator. Therefore this API set represents the object framework used by BrightIntegrator.
BrightIntegrator concepts and how it is configured manually through XML configuration file are documented in the user's manual document provided through the link below. This document explains the main building blocks and the concepts that would be helpful in understanding the API set presented here. Important to note that only a limited small subset of the Job Processor system has been exposed by this API set. Therefore this document needs to be used accordingly only to familiarise oneself with the fundamentals of the job processor concepts.
BrightIntegrator User's Manual
BrightPoint
This object is the helper scripting object for defining table data sources residing in the internal brightdb database (which is a Apache Derby database instance). BrightPoint objects define the internal Derby database where the actual data resides. This object contains sets. Each set corresponds to a Derby database table stored in brightdb.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.bi.BrightPoint) ;
BrightPoint (String name) |
Constructor Parameters: name - Name of the Bright point (also known as the data source name). This is a user defined name that uniquely identifies the defined data source or destination. It is generally a table name. Return Values: BrightPoint- New Bright point object |
void addSet (DatabaseSet set) |
Adds the user defined database set to the Bright point. Each set represents a table. Parameters: set - DatabaseSet object to be added to this memory point.
|
String getQueryName () |
Returns the name of the query to be used for this Bright point. Return Values: String - The name of the query that identifies the database point |
void setQueryName (String queryName) |
Sets the name of the query used by this Bright point object Parameters: queryName - The name of the query |
DatabasePoint
This object is the helper scripting object for defining database data sources. DatabasePoint objects define the database details where the actual data resides. A DatabasePoint object is actually a relational database server access through a JDBC driver. This object defines database connection parameters, and the name of the query object defined in the BEP project to be run against the database. It also contains table sets which are in actual fact database query result sets. Hence each set corresponds to a database table.
The required database attributes can be complicated to configure if one is not familiar with the JDBC lingo. To work around this, one can drag a Database accessor onto a Sync Point in a BEP project, enter the database details as required through the user interface provided. Then the BEP can be exported to a XML by using the BEP project's Export Configuration... pop-up menu option. The exported XML configuration will show the database details such as URL, database driver name etc. for them to be copied into a JavaScript to initialise a DatabasePoint object.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.bi.DatabasePoint) ;
DatabasePoint (String name) |
Constructor Parameters: name - Name of the database point (also known as database data source definition name). This is a user defined name that uniquely identifies the defined database data source or destination. Return Values: DatabasePoint- New database point object |
void addSet (DatabaseSet set) |
Adds the user defined set to the database point. Parameters: set - DatabaseSet object to be added to this database point.
|
String getURL () |
Returns the database URL Return Values: String - Database URL |
String getUserName () |
Returns the database user name Return Values: String - Database user name |
String getPassword () |
Returns the database user password Return Values: String - Database user password |
String |
Returns the database JDBC driver name Return Values: String - JDBC driver name for the database in use |
String getQueryName () |
Returns the name of the query to be used for this database point. Return Values: String - The name of the query that identifies the database point |
void setURL (String url) |
Sets the database URL Parameters: url - New database URL |
void setUserName (String userName) |
Sets the database user name Parameters: userName - Database user name |
void setPassword (String password) |
Sets the database user password Parameters: password - Database user password |
void setDriverName (String driverName) |
Sets the JDBC driver name for the database being used Parameters: driverName - JDBC database driver name |
void setQueryName (String queryName) |
Sets the name of the query used by this database point object Parameters: queryName - The name of the query |
DatabaseSet
A DatabaseSet object represents the records read from the relational database. Those records are identified by the DatabasePoint object's query. In general, the data read from the data points is converted into a set. A set is a very important logical entity within the Job Processor subsystem. It represents the basic processing unit. Data arrives from the source, typically as records from a table, or lines from a file. The incoming data will be formatted and arranged according to the convention of the data source, and will need to be parsed and converted to Bright Software data types. So finally the set will be vendor neutral and de-coupled from the data source, and ready to be processed, and then written to the destination..
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.bi.DatabaseSet) ;
DatabaseSet (String name, String tableName, String mappingName) |
Constructor Parameters: name - Set name tableName - The name of the table defined in the BEP project mappingName - The name of the mapping defined in the BEP project |
String getTableName () |
Returns the table name this set maps to Return Values String - Table name |
String |
Returns the name of the mapping used by the set Return Values String - Name of the mapping used by the set |
FilePoint
This object is the helper scripting object for defining file data sources. FilePoint objects define the file details where the actual data resides. This object contains file sets. Each file set corresponds to a physical text file.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.bi.FilePoint) ;
FilePoint (String name) |
Constructor Parameters: name - Name of the filepoint (also known as database data source name). This is a user defined name that uniquely identifies the defined file data source or destination. Return Values: FilePoint- New file point object |
void addSet (FileSet set) |
Adds the user defined file set to the file point. Each set represents a file. Parameters: set - FileSet object to be added to this file point.
|
FileSet
A FileSet object represents the records read from a file. In general, the data read from the data points is converted into a set. A set is a very important logical entity within the Job Processor subsystem. It represents the basic processing unit. Data arrives from the source, typically as records from the same table, or lines from the same file. The incoming data will be formatted and arranged according to the convention of the data source, and will need to be parsed and converted to Bright Software data types. So finally the set will be vendor neutral and de-coupled from the data source, and ready to be processed, and then written to the destination..
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.bi.FileSet) ;
FileSet (String name, String fileName, String mappingName) |
Constructor Parameters: name - Set name fileName - The name of the file in which the set is stored mappingName - The name of the mapping defined in the BEP project |
String getFileName () |
Returns the name of the file this set is stored in Return Values String - File name |
String |
Returns the name of the mapping used by the set Return Values String - Name of the mapping used by the set |
boolean isAppend () |
Returns if the file is to be appended or not when it is written to Return Values boolean - True if the file is to be appended |
boolean |
Return if the file's first line is the layout headers Return Values boolean - True if the first line is the layout header |
void setAppend (boolean append) |
Return if the file's first line is the layout headers Parameters: append - True to append otherwise false |
void setIncludeHeader (boolean includeHeader) |
Sets the state of the first line in the file. Parameters: includeHeader - True to indicate if the first line is the layout header |
MemoryPoint
This object is the helper scripting object for defining table data sources residing in the internal memory cache. MemoryPoint objects define the internal cached memory database where the actual data resides. This object contains sets. Each set corresponds to a memory table.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.bi.MemoryPoint) ;
MemoryPoint (String name) |
Constructor Parameters: name - Name of the memory point (also known as the data source name). This is a user defined name that uniquely identifies the defined data source or destination. It is generally a table name. Return Values: MemoryPoint- New memory point object |
void addSet (DatabaseSet set) |
Adds the user defined database set to the memory point. Each set represents a table. Parameters: set - DatabaseSet object to be added to this memory point.
|
String getQueryName () |
Returns the name of the query to be used for this memory point. Return Values: String - The name of the query that identifies the database point |
void setQueryName (String queryName) |
Sets the name of the query used by this memory point object Parameters: queryName - The name of the query |
Job
A job is the fundamental operating block in the Job Processor subsystem. It consists of tasks. A task is basically a read action from a data source in order to obtain data, and then a write action to write that data to the destination. The Job Processor creates and maintains the lifetimes of each task configured in a job.
The Job Processor will create the necessary accessors (e.g. database, file etc) to complete the read from the source and subsequent write to the destination. The source accessor is used in the reader mode, and the destination accessor is operated in the writer mode. The accessor configured as the source (i.e. the data reader), reads the data and passes the data as a set to the Job Processor. The Job Processor then writes the set received from the reader to the writer.
The data read from the source is converted into a set. A set represents the basic processing unit. Data arrives from the source, typically as records from the same table, or lines from the same file. The incoming data will be formatted and arranged according to the convention of the data source, and will need to be parsed and converted to Bright Software data types. So finally the set will be vendor neutral and de-coupled from the data source, and ready to be processed, and then written to the destination. When it comes to writing the data to the destination, each set is matched by name from its source to its destination. Each set contains a mapping that provides a name for each field. Each field is also matched by name from within its source set to its destination set. In this way, when transferring data, the set names, and the names of each field within the sets must correspond between source and destination.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.bi.Job) ;
Job (String name) |
Constructor Parameters: name - Name of the job definition |
String getName () |
Returns the name of the job. Return Values String - Job name |
Vector<Task> getTasks () |
Returns the tasks defined in the job. Return Values Vector- Vector of Task objects defined for the job |
void addTask (Task task) |
Adds a new task to the job Parameters: task - New Task object to be added. |
JobManager
JobManager is a helper object for running jobs. A new instance must be created by using ScriptSession.createJobManagerObject() method.
// Create the job manager instance
var jobManager = ScriptSession.createJobManagerObject() ;
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.bi.JobManager) ;
void |
Runs the job. Parameters: : job - Job definition object to be run. |
Task
Task object represents a Job Processor task that forms a part of a job definition. A task is basically a read action from a data source in order to obtain data, and then a write action to write that data to the destination. The Job Processor creates and maintains the lifetimes of each task configured in a job. A job is simply a collection of tasks executed by the Job Processor. See Job object for more details.
Import Statement :
importClass (Packages.au.com.brightsoft.integrator.bi.Task) ;
Task (String name) |
Constructor Parameters: name - Name of the task definition |
String getName () |
Returns the name of the task Return Values String - Task name |
String |
Returns the task description Return Values String - Task description |
DataPoint getSource () |
Returns the source of the data to be read Return Values DataPoint - Data point that contains the source to be read and later written to the destination specified |
DataPoint |
Returns the destination data point to which the data is to be written to Return Values DataPoint - Destination data point to which the data read from the source is to be written to |
DataPoint getOldSource () |
Returns the reference data source that represents the current state of the destination data set. The source will be compared to create a delta (difference) before this delta is written to the destination data point by this task. Return Values DataPoint - Old data source point for calculating the delta, null if not defined |
boolean isBeginTx () |
Checks if this task is the transaction starter Return Values boolean - True for job processor engine to start a transaction |
boolean isEndTx () |
Checks if this task ends the current transaction Return Values boolean - True for job processor engine to end the current transaction |
void setBeginTx (boolean bt) |
Marks the task to start a transaction when the job is being executed Parameters: bt - True to mark the start of the transaction |
void setEndTx (boolean et) |
Marks the task to end the current transaction when the job is being executed Parameters: et - True to mark the end of the transaction |
void setSource (DataPoint source) |
Sets the data point object to be used as data source for the task Parameters: source - The data point the data is to be read from |
void setDestination (DataPoint destination) |
Sets the data object to be used as the data destination for the task Parameters: destination - The data point the data is to be written to |
void setOldSource (DataPoint oldSource) |
Returns the data source that is the previous state of the data. The new source data point will be compared to this data set to create a new delta for processing. This way the task can figure out what has changed (added, modified, or deleted) and can quickly process the data writing process to the specified data destination. Parameters: oldSource - Reference data source. This is the assumed state of the current destination data set. |
void setDescription (String description) |
Sets the task description Parameters: description - Task description |
