Binary Data in BrightForms
Contents Hide
Base64Binary Data
Binary data in records may be synchronised to and from BrightServer via the 'base64Binary' type for both BSP and BEP tables.
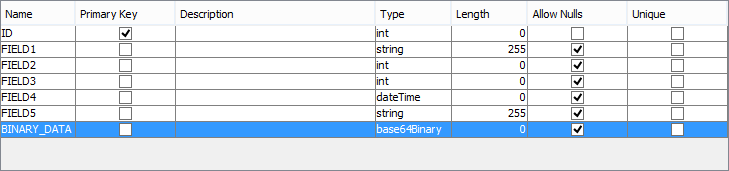
This will synchronise the binary data for each record into the device's database and vice versa. In BrightForms, data may be read from database columns into controls, such as scribble and images, and variables by querying the database.
An example is as follows:
qRecordById.pId = local.vId;
image1 = qRecordById.BINARY_DATA;
Data received from the device may be written directly to server binary database columns, such as BINARY or IMAGE, and then read via external processes and applications accordingly.
 Scribble
data is additionally compressed when read from the control. While
Scribble and Image controls may read and display both compressed
and uncompressed data, if this data is to be read from the database
outside of BrightForms or BrightWeb, it is recommended to either
be decompressed on the device before it is written to the database
(by Zip.UnzipBinary()), or have mapping
specified to decompress this data when it synchronises to
the server.
Scribble
data is additionally compressed when read from the control. While
Scribble and Image controls may read and display both compressed
and uncompressed data, if this data is to be read from the database
outside of BrightForms or BrightWeb, it is recommended to either
be decompressed on the device before it is written to the database
(by Zip.UnzipBinary()), or have mapping
specified to decompress this data when it synchronises to
the server.
The following code will write image data loaded from a file into the device's local database. After this is synchronised to the server, the image data may then be read from the BINARY_DATA column as-is.
local.imgFile = Camera.GetFileName();
local.vData = File.LoadBinary(local.imgFile);
Database.Reset();
Database.SetQueryParam("pId", local.vId);
Database.AddColumn("BINARY_DATA", local.vData);
Database.UpdateRecords("qRecordById");
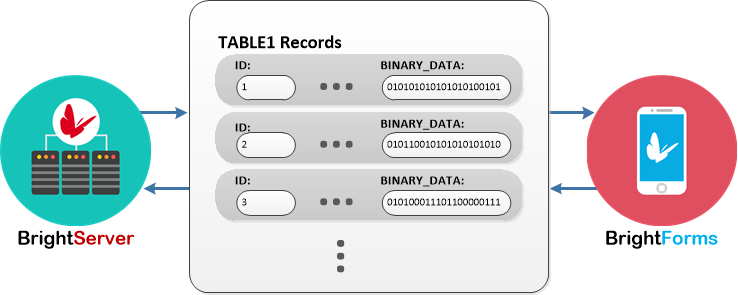
As the binary data is stored within the record, the sync engine will synchronise these records as-is to/from the server. While groups of these records will be sent based on the Data Size Limits of the server, at least one record must be sent each time using this feature. This may result in packet sizes larger than the maximum size being transmitted to and from the server if large amounts of data exist in the columns on either the device and server.
As such, rather than the base64Binary type, the externalBlob data type should be used if large binary data is required to be sent/received for each record between server and client. This is detailed below.
External Blob
Binary data may also be defined as an 'externalBlob' type for server or device columns.
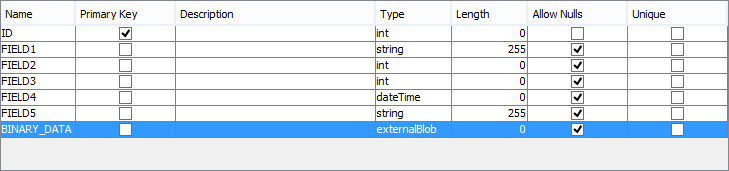
Data in this table column is stored as a String, which will specify a full file path to a file containing the binary data. Synchronising this path with the 'externalBlob' type, will chunk the file to be transmitted based on the Data Size Limits of the server. The packets of the file will then be sent to the device/server destination.
Once the file has been confirmed to be transmitted successfully, the record will be written to the device with the path in the field updated with the local file.
Synchronising files using the externalBlob type will reduce the database size and memory footprint of the application when performing synchronisation and database operations. It also allows easier transmission of end user resources, if they are to be accessed via external means, such as pdf files, videos etc.
Below are the specifics of the externalBlob synchronisation, for when data is sent from either the Server or the Client.
Server to Client
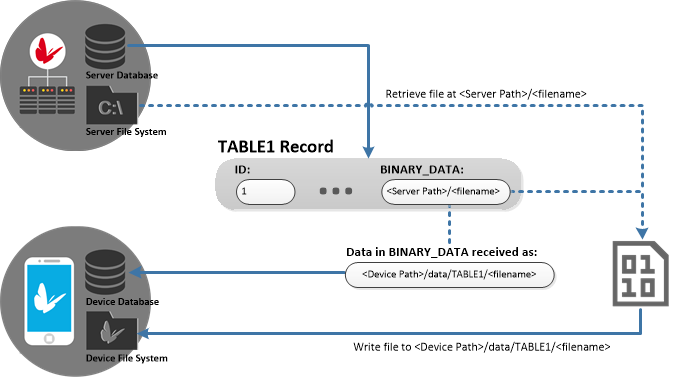
The above diagram shows the process for a server to device synchronisation. The path stored in the source database in this scenario may be any file accessible to BrightServer on the server, such as:
C:\data\image001.jpg
During the synchronisation, BrightForms will write the file sent by the server to the 'data' folder of the devices project directory, in sub-directories specifying the table name and column name. For example, the file sent from the path above would be written to the local, device path below:
<project directory>/data/TABLE1/image001.jpg
If a file already exists in this location, it will be overwritten. Once received, expressions may be used in BrightForms to access the files, based on the path retrieved from the database. For example:
qRecordById.pId = local.vId;
local.imgPath = qRecordById.BINARY_DATA;
image1 = File.LoadBinary(local.imgPath);
This will query the database for the local path, then load the binary data into the image1 control.
Please note, if file changes occur on the server, synchronising the same record will overwrite the file on the device with the latest version from the server. Thus, if the user is to also modify these files, a copy should be made such that editing is outside of the data directory, such that they will not be overwritten if updated on the server.
Client to Server
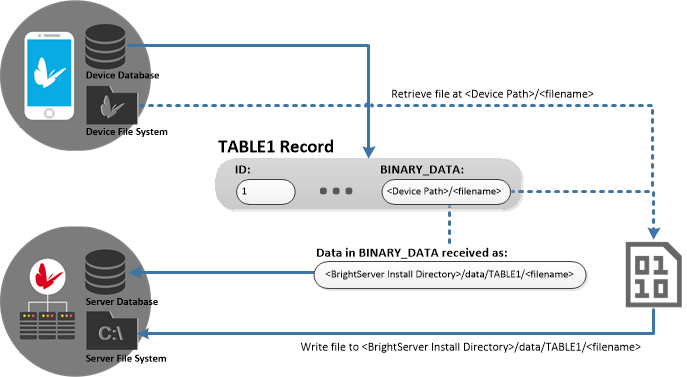
The above diagram shows the process of synchronising externalBlob data from the device to BrightServer. The file may be located on the device in any directory accessible to BrightForms, such as:
<project directory>/image001.jpg
When synchronised to the server, similar to the server to device synchronisation, when BrightServer receives the file from client devices, it will write them to the 'data' folder in its installation directory, under table and column name sub-directories:
<BrightServer install directory>/data/TABLE1/image001.jpg
The 'data' folder is used by default, but this may be changed via the --datadir flag via BrightServer Command Line options.
If the file exists, it will be overwritten. As multiple users may potentially synchronise to a server table, it is important to ensure that where required, file names are unique such that they do not get overwritten on the server. This may be achieved by utilising a GUID or a combination of keys for the filename, and possibly a suffix for the table column. For example:
local.imgFile = Camera.GetFileName();
local.vUniqueFile = "BINARY_DATA"
& System.GetProjectPath() & "/" & NumberGenerator.GetGUID()
& ".jpg";
local.vResult = File.RenameFile(local.imgFile, local.vUniqueFile);
IF (local.vResult == 0)
{
Database.Reset();
Database.SetQueryParam("pId", local.vId);
Database.AddColumn("BINARY_DATA", local.vUniqueFile);
Database.UpdateRecords("qRecordById");
}
externalBlob Notes
Please note the following when using the externalBlob data type for synchronisation:
The externalBlob data type is available to database sync sources only. Other data sources will simply synchronise the string as-is with no file data to the device.
If the file data fails to send, the sync will fail, and the record will not be added to the destination database.
If the file cannot be found on the server/device, NULL will be recorded in the externalBlob field.
If a file already exists on either the server or client's destination directory, it will be overwritten.
NULL will be synchronised as-is to the destination table record.
The file name for both server and device has a limit of 2048 characters.
