Global Elements
Contents Hide
The Globals element allows you to create and define global variables, global expressions, user defined constants and global menus. These objects can be accessed and used by any form in the project.
Global Variables
A global variable is a variable that can be used within the project scope. This means that it can be accessed from anywhere in the project. Any of the forms can have access to this variable. They retain their values while the project is open.
Global variables are declared and defined within the project context.
Global Variable behave similarly to App Settings, however App Settings are stored on a local text file within the BrightForms export directory, thus there is more overhead in using App Settings than global variables. Global variables are stored in memory at runtime and are lost when the application is closed, whereas App Settings values are persisted in a file and values can be reused when the application is run again.
Using the same names for a global and form variable will not create any ambiguity in the application as form expressions references a global variable with a global label and dot notation.
E.g. global.Variable1, global.VarTempString, global.IntID.
A good reason to use global variables is to avoid having to pass frequently-used variables continuously between forms. But the disadvantage is that potentially it can be modified from anywhere and any part of the application may depend on it. Thus it is good programming practice to use local variables whenever possible and use global variables only when absolutely needed.
Creating Global Variables
To create a global variable follow these steps:
Double-click the Globals element to open on the Globals editor window.
Go to the Variables tab.
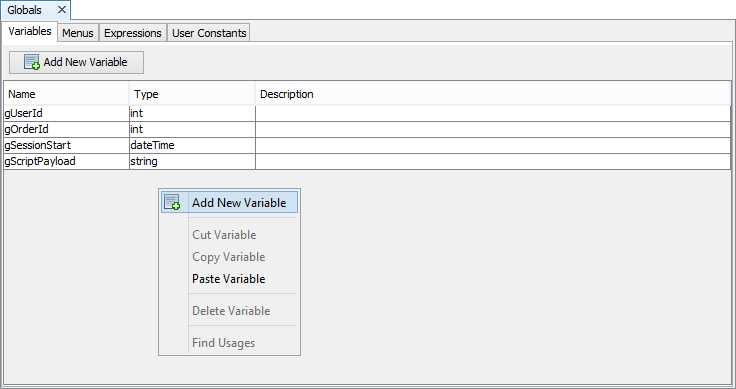
Right-click inside the Variables window.
Select Add New Variable from the pop-up menu.
Rename the Variable as required by the application.
Specify the data type. Description is optional.
Using Global Variables
To use a global variable within an expression,
Create an expression
Expand the Data Source tree.
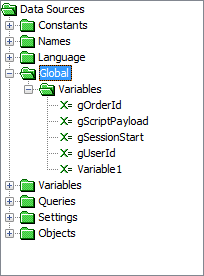
Go to Data Sources>Global>Variables if it is a global expression. Go to Data Sources > Form> Variables > Globals if it is a form expression.
Drag the global variable inside the expression. Or if using the Text Editor, simply type <VariableName > if its a global expression, else global.<VariableName> if its a form expression.
Global Menus
Global menus are menus which may be used on any form in the project. Each form has the option of displaying one or more global menus.
Creating Global Menus
To create a global menu:
Open the Globals element.
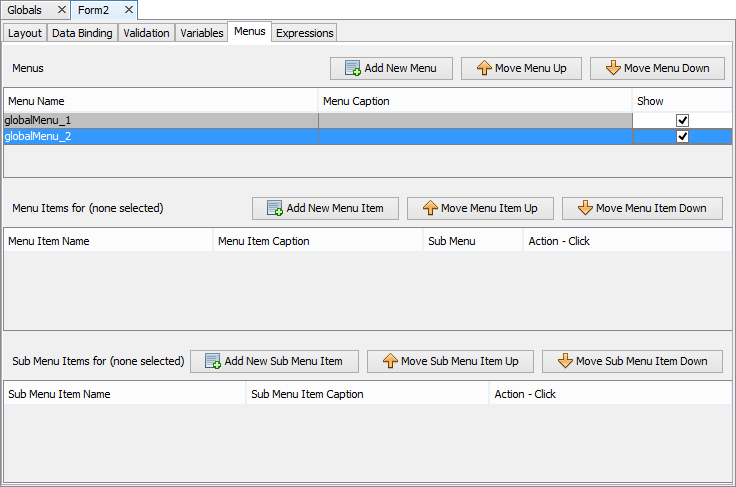
Go to Menus tab. This is exactly the same as any form menu panel.
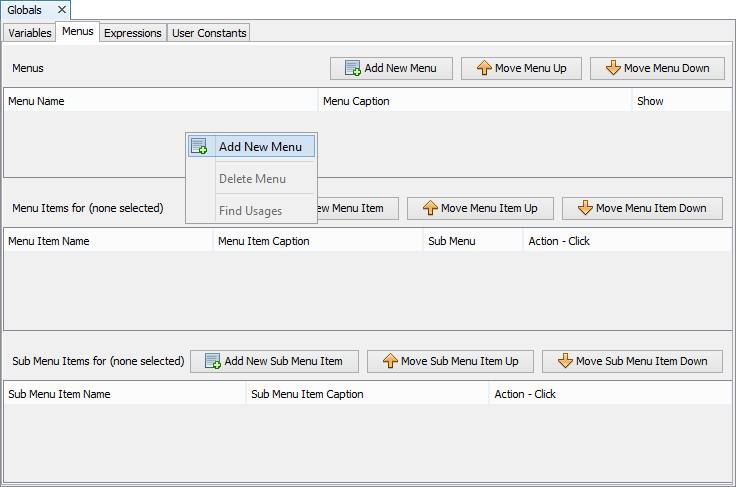
Create a new menu along with any sub menus and items. For more help with creating menus, please see Chapter 10: Forms.
Using Global Menus
To have a global menu show in a form:
Open the form and select the Menus tab.
All the global menus will automatically be shown on the Menus list. By default these are all set to be hidden.
Tick the Show checkbox for any menus that should be shown on the form.
Global Expressions
Global expressions are functions that can be used throughout the project. Any form or form control actions can execute this expression. It can also be called within a form expression.
Creating Global Expressions
To create a global expression:
Open the Globals element.
Go to Expressions tab. As you can see this is exactly the same as any form expression editor.
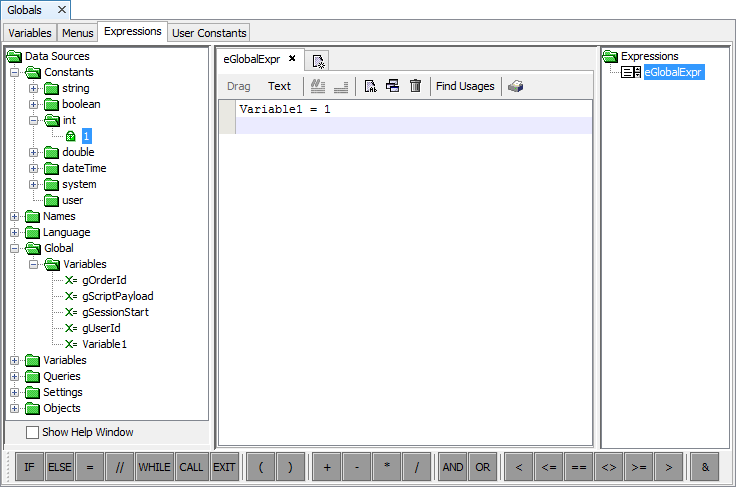
Create a new expression.
Drag and drop the expression statements or simply use the Text Editor to type your expression statements.
Using Global Expressions
To select a global expression as a form action,
Select the form action property to modify, Action Open for example.
Click on the drop-down button to display the expression list that can be accessed by this action.
Select global.<expressionName> from the list.
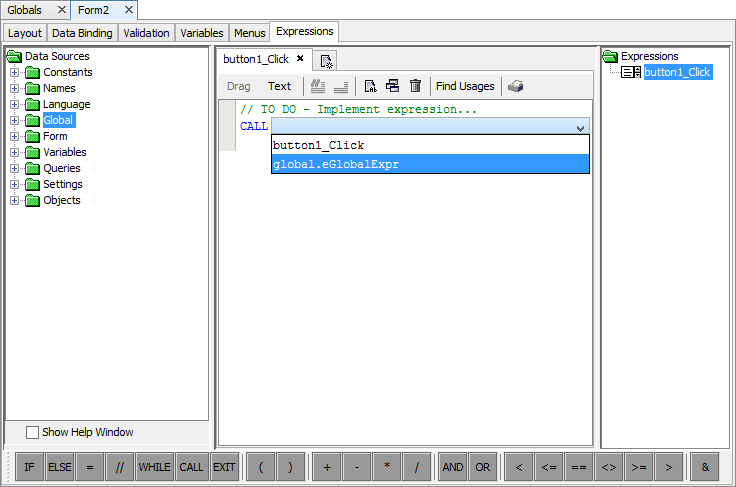
 NOTE: Global expressions are prefixed with the "global"
qualifier to differentiate them from form expressions.
NOTE: Global expressions are prefixed with the "global"
qualifier to differentiate them from form expressions.
User Constants
User Constants are strongly typed constants. They are essentially unique types that allow you to assign symbolic names to any value. This allows you to have a maintainable code because they are symbolic, allowing you to work with different data types such as integral values, but using meaningful names to do so.
For example, instead of using integer values 0,1,2, and 3 you can use the set of values named North, South, East and West to denote these numbers within your code.
User defined constants scope is the same as that of the Global Variables. You can use these user constant in any form expressions in the project.
You can define a user constant through the Globals element. Accessing the user constants from the Data Source would be through Data Sources > Constants> user sub tree.
Creating User Constants
To create a User Constant:
Double-click on the Globals element to open it in the Editor window, and select the User Constants tab.
Tap on the 'Add New Constant Group' button, or right-click on the Name window, then select 'Add New Constant Group' from the pop-up menu. A new User Constant group will be created - 'UserConstantGroup1'.
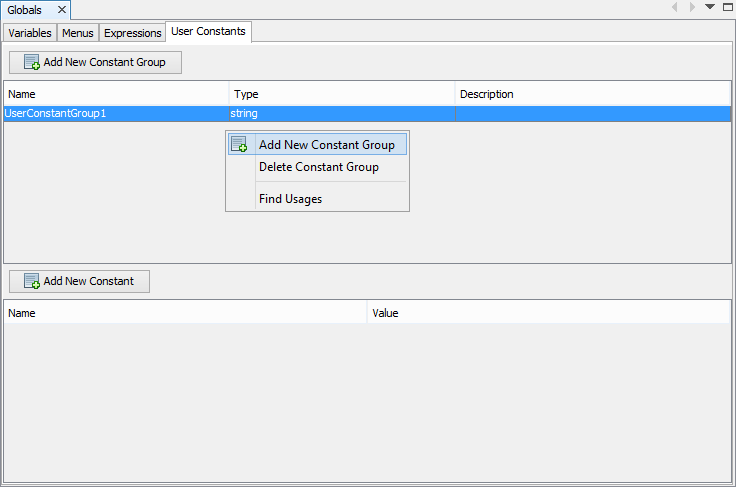
Rename the User Constant Group by double tapping the 'Name' cell of the control. All fields in both the Constant Group and Constants tables may be edited by double clicking cells.
Change the type of the constant group to either String or Int, depending on the value(s) required.
Tap on the 'Add New Constant' button, or select the context menu option from the Constants (lower) table. A new constant will be created called 'UserConstant1'.
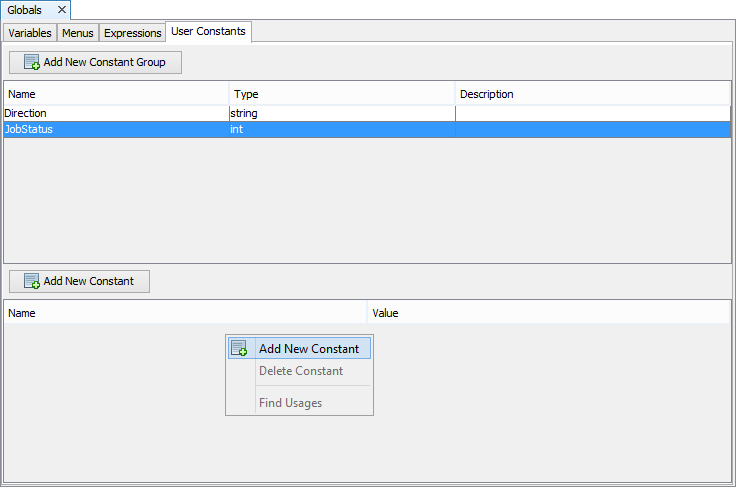
Create more user constants if required
Double tap the constant's 'Name' cell to rename User Constants if required.
Similarly, double tap the constant's 'Value' cell to define the value of the user constant.
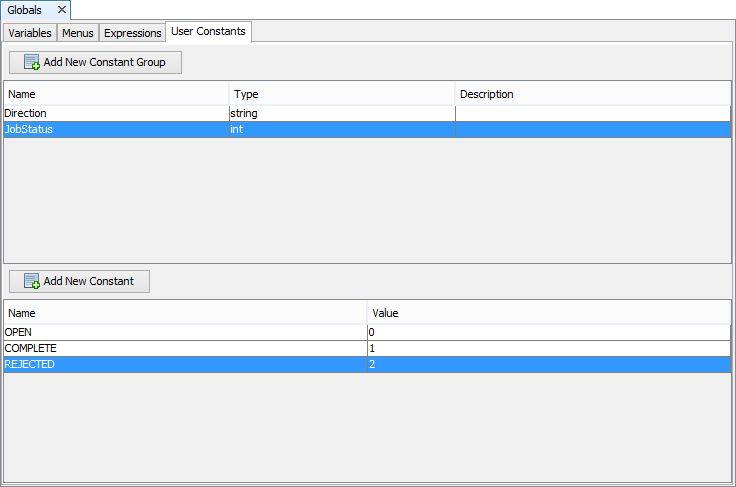
Below is an example of the User Constants tab with two User Constant Groups.
Using User Constants
To use the User Constants in an expression:
Create an expression
Select Data Sources > Constants > user > <UserConstantGroup> > < UserConstantName> and drag inside the expression.
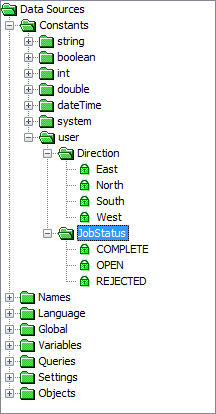
From the image above, if East was assigned to Variable1, the expression will contain the expression statement:
Variable1=Direction.East
Notice how the expression line consist of the user constant group name and user constant value. You can use the same format if typing an expression in TEXT mode.
 Note: Although constants somewhat resemble variables, you
cannot modify them or assign new values to them as you can
to variables.
Note: Although constants somewhat resemble variables, you
cannot modify them or assign new values to them as you can
to variables.
