Quick Tutorial - How to Use Remote Procedure Calls
Description
This tutorial will explain how to set up, end-to-end, a remote procedure call to the server from a client device.
Introduction
The BrightXpress mobility suite provides a flexible framework for end-to-end application development, with many methods to synchronise and retrieve data to and from the server database.
Online queries are one such tool, allowing an application to bypass a full sync to retrieve data from the server, reducing any unnecessary overhead when only a certain subset may be needed. It also may provide a snapshot of potentially constantly changing data on the server side for any application. This online query property can be activated for any Standard and Advanced SQL record sets.
There is also further support in the BrightXpress mobility suite for online queries, in the form of Stored Procedures and Remote Procedure Calls (RPC). They are exclusively online, and acts as a low overhead operation which still enables developers to incorporate specific routines for their mobile application through the server, process any range of inputs, outputs to and from the server, with addition to a record set if necessary.
Setting up an RPC is in the form of a script and located and executed on BrightServer rather than the database. This script accepts input parameters via the executeRPC() function, and may may interface with a range of sources, including a database itself. The script's function will then return parameters and outputs to BrightServer, which will then send the online query resultset to BrightForms. All of this occurs over BrightServer's sync engine.
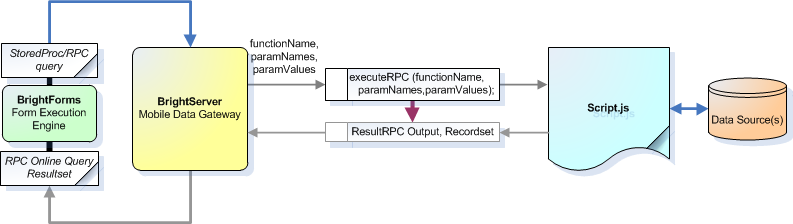
An RPC's functionality may encompass that of database stored procedures, yet also having additional flexibility being able to utilise BrightServer's powerful scripting engine. This tutorial will demonstrate how to establish an RPC on the server, and how to call it in the application. This is done by:
Setting up the BEP's script and sync point, and
Setting up the BSP's queries, data sources and point of execution
A sample configuration and application is also provided, demonstrating this process.
BEP Setup
Creating the RPC script
User defined sync points are written in JavaScript, and exist as code within projects that get executed at runtime by the server. An RPC is a type of script, and must firstly be defined within in the BEP under the scripts node.
A valid RPC script must have the function executeRPC() to run correctly, a template of which is available when creating a new script via the context menu. This executeRPC method will be called by the application, and have input and output parameter values passed to it via arrays. A function name will also be specified. After processing, the script function will return a ResultRPC object, which will consist of output fields and a record set. An example of this is as follows:
function executeRPC(functionName, paramNames, paramValues)
{
ScriptSession.logInfo("Executing RPC");
// Extract the input parameter(s)
pUserId = paramValues.get(0);
pAddNew = paramValues.get(1);
// Create a new ResultRPC to return
result = new ResultRPC();
// Assign an output parameter the string value "Example"
result.setOutputParameter ("pOutputName", "Example");
// Create a new record set, and assign to result
rs = new RecordSet("OUTPUT_RECORDSET");
// ...
result.setRecordSet(rs);
// Return the ResultRPC object
return result;
}
 Note:
One use of scripts may be an alternate means to connect to
the database, where conventional synchronisation, or even
database stored procedures may not be appropriate. For more
information, please refer to the Using
JDBC in Scripts tutorial.
Note:
One use of scripts may be an alternate means to connect to
the database, where conventional synchronisation, or even
database stored procedures may not be appropriate. For more
information, please refer to the Using
JDBC in Scripts tutorial.
For more information on the structure of an RPC script, please also refer to the BrightServer > Scripts > RPC (Remote Procedure Calls) chapter of the documentation.
Establishing a Sync Point
Once defined, the script may then be set up as a sync point on the server via the sync panel of a BEP BrightServer configuration project. This is done by dragging and dropping the script icon into the sync space, and naming the script via the 'Script' property. As RPCs are an online process, the sync point does not need to be associated with a client table, but it must be exposed as a data source to BrightServer for these online operations to occur.
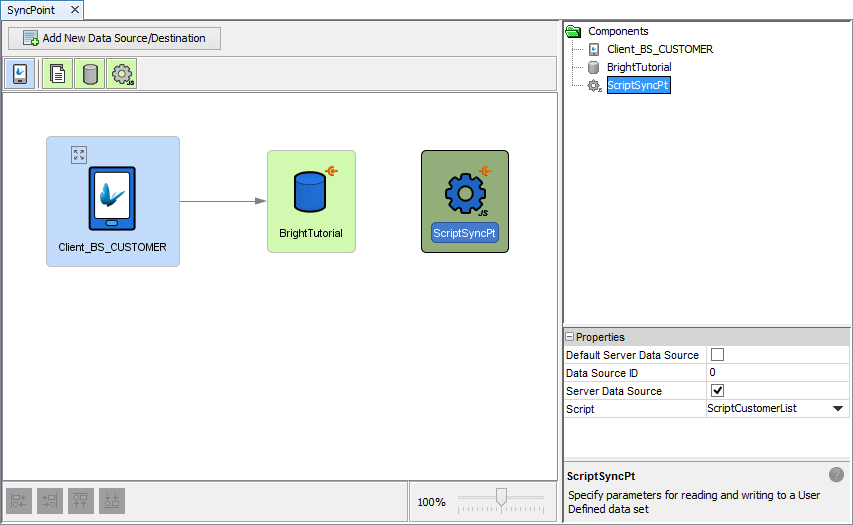
Whether or not a sync point is a server data source is configured via the 'Server Data Source' property. Once set, this property is represented by the their sync point with an orange icon at the top right. Setting this property to 'true' will expose the sync point as a server data source, allowing the return of 'flat' recordsets to BrightForms applications.
If there is more than one server data source, each will need to be assigned a unique ID. This is also specified in the sync point's properties panel, and is a numeric value. Online queries have a data source they operate upon, 'directing' them to the particular data source, based on this ID. The 'Default Server Data Source' option may also be set to true to have this source accessible when an ID is not specified by the application.
With the BEP set up, the application will then define queries and sync rules in accordance to these sync points, which will be explained in the following section.
BSP Setup
With the BrightServer configuration set up and running, Online Stored Procedure queries are established by setting properties in the Queries Panel of a project, and specifying parameters and outputs of those queries in BrightBuilder. The query may then be assigned to a sync rule, which, when run, will interface with the BrightServer script and populate the output parameters and the resultset of the query.
Setting up a new query
Create a new query of the type 'Stored Procedure/RPC". As this type of query is online only, BrightBuilder will automatically set the 'online query' property to true. This may be confirmed, as a query set to online will have its element icon in the projects tree turn red. If this is not checked, the project have a validation error once the project is deployed or released.
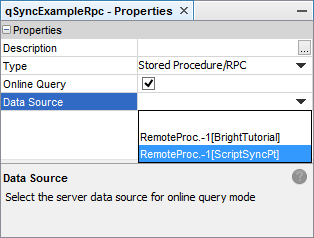
While this process will define that a stored procedure or a RPC will be used, it does not define which one will run, and on what data source. For this to be established, the query's Data Source from BrightServer needs to be defined, and these sources need to be discovered for the project. If no source is specified, the server's default data source will be used.
Discovering Server Sources
Every online query must refer to a Data Source for its data, either defined explicitly or using the default data source in a BEP configuration.
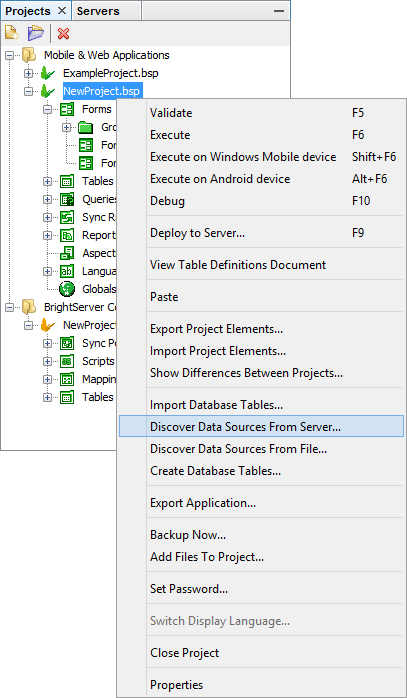
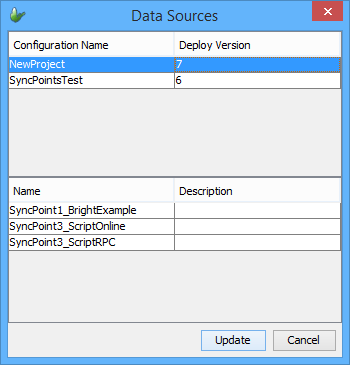
Right clicking a project will display the option to discover data sources either from the server or files. Selecting 'server' will connect to a server, and retrieve a list of exposed data sources from the server's configuration, displaying the results in a dialog. The 'files' option will do this from opened BEP projects. Upon tapping the 'update' button, the BSP will register the sources into the project. Once registered, these data sources may be assigned to queries via drop down menu.
Defining the query
Once the destination of the query has been defined with the query's data source, the particulars such as the inputs, outputs and records returned my be specified. This may be done with the query's panel of BrightBuilder.
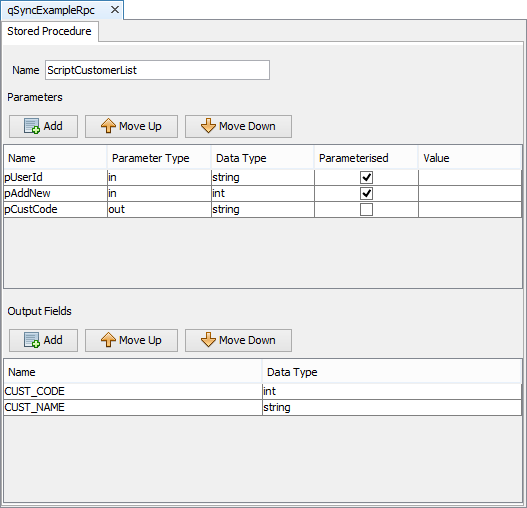
When this screen opens, the actions available are follows (top to bottom):
The 'function name' of the to be passed to BrightServer script. This allows for a single script to have multiple functionality, depending on the name given.
Define input, output, and (single) in/out parameters. Inputs/In-Outs may be parameterised, and when ticked appear in the DST, or they may be static and defined as inputs.
Define output result set. This may consist of any number of columns, and must match the result set returned by the stored procedure/RPC.
Running the Query in an Application
For data to be passed, processed and retrieved from the device, sync rule must be run for the query. The inclusion of the sync rule and the execution of the sync rule itself is the same as any other query - the rule must be called after a Synchroniser.Connect() method, or enabled prior to then executed a Form.ShowSyncDialog() method, and as with any parameterised sync, input parameters need to be specified together with the sync rule, such as via globals.
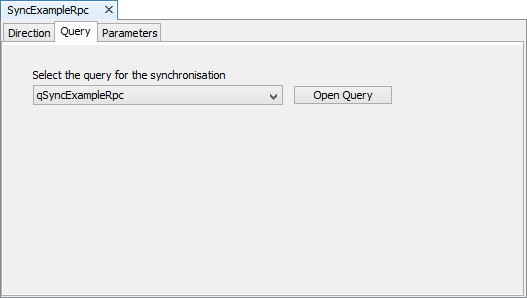
An example of a sync rule running for the online query is as follows:
// The following code will run the stored procedure via the sync dialog
Synchroniser.DisableAll();
Synchroniser.EnableSyncRule("SyncExampleRpc", true);
Form.ShowSyncDialog(false);
One the sync rule runs, any in/out or output parameters will be populated, and any subsequent reference to the query will use the recordset returned. Its previous results will be discarded. As the result set is static, the most common place for it to be displayed is via a listview or combobox. Records may also be traversed via the Query object.
// The following is run after the sync rule executes, thus populating the output fields
editCustCode = qSyncExampleRpc.pCustCode;
// refresh listview containing the query, will be updated with most recently retrieved resultset
listview1.refresh();
Please note, that there is a limited number of records the server may return to the device. This figure is based on BrightServer's configuration, with the default being 200 records. For more information, please refer to BrightServer > Server Settings > Data Size Limits.
Exercise
Application
The example is of an application which allows the end user (with user number 42) to create a new customer record, whose ID is uniquely populated by the server. This may be necessary if the application required customer numbers to be created on the fly and be unique, but also requires its use as a reference in many records.
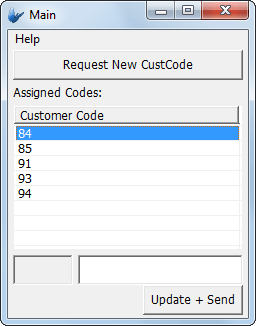
The user may then assign a name to the record ID, and the record is sent to the server on the 'Update + Send' button tap. After sending the data once more, the list of assigned IDs is then refreshed from the server, and displayed.
BEP File
The creation of new customers and assignment of codes to PDA users is handled by the BrightServer RPC script 'ScriptCustomerList'. Both the creation and retrieval of assigned records is handled by the same RPC, with the device specifying if it needs a new record, or to simply retrieve the list via an input parameter. Once the customer codes have been retrieved by the device, the application may be used to update the records based off this code via conventional synchronisation.
To set the BEP up, create a database on localhost named "BrightTutorial". Run the RemoteProcCreate_tbl.sql script on this newly created database to create the Customer table that the sample application will use.
The database utilised by the script needs to be configured within the BEP itself. To do this, Open up the BEP, and locate the following code in the ScriptConnection.getConnection() method:
// Script constants
var sqlConnectionString= "jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;DatabaseName=BrightTutorial";
var sqlUsername = "<username>" ;
var sqlPassword = "<pass>";
Substitute <username> and <password> strings with the username and password assigned for the BrightTutorial database.
After completing the above, execute the BEP server configuration or deploy/activate it on a BrightServer instance.
BSP File
After opening RemoteProcStart.bsp in BrightBuilder, complete the exercise by linking the BSP's queries, sync rules and listview control to the BrightServer instance set up, as defined by the BrightServer configuration. Review where necessary the executeRPC() method in the 'ScriptCustomerList' script for the inputs/outputs of each to transfer into the BSP.
A possible solution is available in RemoteProcFinished.bsp.
